Appendix IV B. Colour of Solution
The examination of the degree of coloration of liquids in the range brown-yellow-red is carried out by one of the 2 methods below, as prescribed in the monograph.
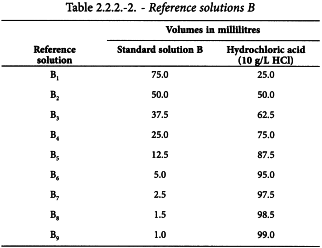
A solution is colourless if it has the appearance of water R or the solvent or is not more intensely coloured than reference solution B9.
METHOD I
Using identical tubes of colourless, transparent, neutral glass of 12 mm external diameter, compare 2.0 mL of the liquid to be examined with 2.0 mL of water R or of the solvent or of the reference solution (see Tables of reference solutions) prescribed in the monograph. Compare the colours in diffused daylight, viewing horizontally against a white background.
METHOD II
Using identical tubes of colourless, transparent, neutral glass with a flat base and an internal diameter of 15 mm to 25 mm, compare the liquid to be examined with water R or the solvent or the reference solution (see Tables of reference solutions) prescribed in the monograph, the depth of the layer being 40 mm. Compare the colours in diffused daylight, viewing vertically against a white background.
REAGENTS
Primary solutions
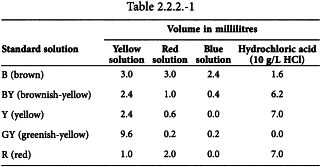
Yellow solution Dissolve 46 g of ferric chloride R in about 900 mL of a mixture of 25 mL of hydrochloric acid R and 975 mL of water R and dilute to 1000.0 mL with the same mixture. Titrate and adjust the solution to contain 45.0 mg of FeCl3,6H2O per millilitre by adding the same acidic mixture. Protect the solution from light.
Titration. Place in a 250 mL conical flask fitted with a ground-glass stopper, 10.0 mL of the solution, 15 mL of water R, 5 mL of hydrochloric acid R and 4 g of potassium iodide R, close the flask, allow to stand in the dark for 15 min and add 100 mL of water R. Titrate the liberated iodine with 0.1 M sodium thiosulfate, using 0.5 mL of starch solution R, added towards the end of the titration, as indicator.
1 mL of 0.1 M sodium thiosulfate is equivalent to 27.03 mg of FeCl3,6H2O.
Red solution Dissolve 60 g of cobalt chloride R in about 900 mL of a mixture of 25 mL of hydrochloric acid R and 975 mL of water R and dilute to 1000.0 mL with the same mixture. Titrate and adjust the solution to contain 59.5 mg of CoCl2,6H2O per millilitre by adding the same acidic mixture.
Titration. Place in a 250 mL conical flask fitted with a ground-glass stopper, 5.0 mL of the solution, 5 mL of dilute hydrogen peroxide solution R and 10 mL of a 300 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R. Boil gently for 10 min, allow to cool and add 60 mL of dilute sulfuric acid R and 2 g of potassium iodide R. Close the flask and dissolve the precipitate by shaking gently. Titrate the liberated iodine with 0.1 M sodium thiosulfate, using 0.5 mL of starch solution R, added towards the end of the titration, as indicator. The end-point is reached when the solution turns pink.
1 mL of 0.1 M sodium thiosulfate is equivalent to 23.79 mg of CoCl2,6H2O.
Blue primary solution Dissolve 63 g of copper sulfate pentahydrate R in about 900 mL of a mixture of 25 mL of hydrochloric acid R and 975 mL of water R and dilute to 1000.0 mL with the same mixture. Titrate and adjust the solution to contain 62.4 mg of CuSO4,5H2O per millilitre by adding the same acidic mixture.
Titration. Place in a 250 mL conical flask fitted with a ground-glass stopper, 10.0 mL of the solution, 50 mL of water R, 12 mL of dilute acetic acid R and 3 g of potassium iodide R. Titrate the liberated iodine with 0.1 M sodium thiosulfate, using 0.5 mL of starch solution R, added towards the end of the titration, as indicator. The end-point is reached when the solution shows a slight pale brown colour.
1 mL of 0.1 M sodium thiosulfate is equivalent to 24.97 mg of CuSO4,5H2O.
Standard solutions
Using the 3 primary solutions, prepare the 5 standard solutions as follows (Table 2.2.2.-1):
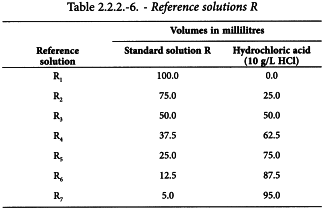
Reference solutions for Methods I and II
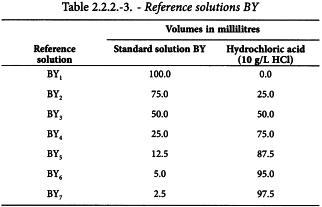
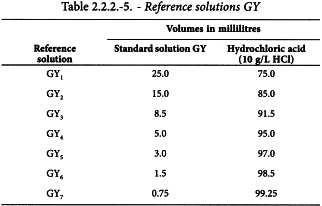
Using the 5 standard solutions, prepare the following reference solutions.
Storage
For Method I, the reference solutions may be stored in sealed tubes of colourless, transparent, neutral glass of 12 mm external diameter, protected from light.
For Method II, prepare the reference solutions immediately before use from the standard solutions.