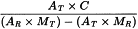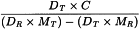Appendix VIII M. Residual Ethylene Oxide and Dioxan
The test is intended for the determination of residual ethylene oxide and dioxan in samples soluble in water or dimethylacetamide. For substances that are insoluble or insufficiently soluble in these solvents, the preparation of the sample solution and the head-space conditions to be employed are given in the individual monograph.
Head-space gas chromatography (2.2.28).
Test solution Weigh 1.00 g (MT) of the substance to be examined in a 10 mL vial (other sizes may be used depending on the operating conditions) and add 1.0 mL of water R. Close and mix to obtain a homogeneous solution. Allow to stand at 70 °C for 45 min.
Reference solution (a) Weigh 1.00 g (MR) of the substance to be examined into an identical 10 mL vial, add 0.50 mL of dioxan solution R2 and 0.50 mL of ethylene oxide solution R3. Close and mix to obtain a homogeneous solution. Allow to stand at 70 °C for 45 min.
Reference solution (b) To 0.50 mL of ethylene oxide solution R3 in a 10 mL vial add 0.1 mL of a freshly prepared 10 mg/L solution of acetaldehyde R and 0.10 mL of dioxan solution R1. Close and mix to obtain a homogeneous solution. Allow to stand at 70 °C for 45 min.
Test solution Weigh 1.00 g (MT) of the substance to be examined in a 10 mL vial (other sizes may be used depending on the operating conditions) and add 0.20 mL of water R and 1.0 mL of dimethylacetamide R. Close and mix to obtain a homogeneous solution. Allow to stand at 90 °C for 45 min.
Reference solution (a) Weigh 1.00 g (MR) of the substance to be examined into an identical 10 mL vial, add 0.10 mL of dioxan solution R1, 0.10 mL of ethylene oxide solution R2 and 1.0 mL of dimethylacetamide R. Close and mix to obtain a homogeneous solution. Allow to stand at 90 °C for 45 min.
Reference solution (b) To 0.10 mL of ethylene oxide solution R2 in a 10 mL vial, add 0.1 mL of a freshly prepared 10 mg/L solution of acetaldehyde R and 0.10 mL of dioxan solution R1. Close and mix to obtain a homogeneous solution. Allow to stand at 70 °C for 45 min.
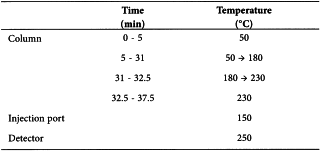
material: glass or fused silica;
Carrier gas helium for chromatography R or nitrogen for chromatography R.
Linear velocity 20 cm/s.
Split ratio 1:20.
Detection Flame ionisation.
Injection A suitable volume, for example 1.0 mL, of the gaseous phase of the test solution and of reference solutions (a) and (b). Repeat the procedure twice more.
Verification of precision
For each pair of injections, calculate for ethylene oxide and for dioxan the difference in area between the peaks obtained with the test solution and reference solution (a). The test is not valid unless the relative standard deviation of the 3 values obtained for ethylene oxide is not greater than 15 per cent and the relative standard deviation of the 3 values obtained for dioxan is not greater than 15 per cent. If the weighings used for the test solution and reference solution (a) differ from 1.00 g by more than 0.5 per cent, the appropriate corrections must be made.
Calculate the content of ethylene oxide or dioxan in parts per million from the following expressions:
| AT | = | area of the peak due to ethylene oxide in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution; |
| AR | = | area of the peak due to ethylene oxide in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a); |
| MT | = | mass of the substance to be examined in the test solution, in grams; |
| MR | = | mass of the substance to be examined in reference solution (a), in grams; |
| C | = | amount of ethylene oxide added to reference solution (a), in micrograms. |
| DT | = | area of the peak due to dioxan in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution; |
| DR | = | area of the peak due to dioxan in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a); |
| C | = | amount of dioxan added to reference solution (a) in micrograms. |