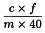Appendix VIII R. Nickel in Hydrogenated Vegetable Oils
Atomic absorption spectrometry (2.2.23, Method I).
CAUTION: when using closed high-pressure digestion vessels and microwave laboratory ovens, be familiar with the safety and operating instructions given by the manufacturer.
The reagents magnesium nitrate R and ammonium dihydrogen phosphate R must be controlled for nickel before use. The actual nickel content is taken into account in the calculation of the nickel content of the sample.
Test solution Weigh 0.250 g (m) of the substance to be examined into a suitable high-pressure-resistant digestion vessel (fluoropolymer or quartz glass), add 6.0 mL of nickel-free nitric acid R and 2.0 mL of strong hydrogen peroxide solution R. Prepare a blank solution in the same manner. Place the closed vessels in a laboratory microwave oven and digest with an appropriate programme, e.g. 1000 W for 40 min. Allow the digestion vessels to cool before opening. Add 2.0 mL of strong hydrogen peroxide solution R and repeat the digestion step. Allow the digestion vessels to cool before opening. Quantitatively transfer to a 25 mL flask, add 0.5 mL of a 10 g/L solution of magnesium nitrate R and 0.5 mL of a 100 g/L solution of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate R, dilute to 25.0 mL with water for chromatography R and mix.
Reference solutions Into 4 volumetric flasks, introduce 25 µL, 50 µL, 75 µL and 100 µL of nickel standard solution (5 ppm Ni) R. To each flask, add 0.5 mL of a 10 g/L solution of magnesium nitrate R, 0.5 mL of a 100 g/L solution of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate R and 6.0 mL of nickel-free nitric acid R and dilute to 25.0 mL with water for chromatography R. Mix to obtain reference solutions containing respectively 5 ng/mL, 10 ng/mL, 15 ng/mL and 20 ng/mL (ppb) of nickel.
Zero solution In a volumetric flask, introduce 1.0 mL of a 10 g/L solution of magnesium nitrate R, 1.0 mL of a 100 g/L solution of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate R and 12.0 mL of nickel-free nitric acid R. Dilute to 50.0 mL with water for chromatography R and mix.
Method Determine the absorbance of each solution at 232.0 nm using a suitable graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometer equipped with a background compensation system, a pyrolytically-coated tube, and a nickel hollow-cathode lamp. Maintain the drying temperature of the furnace at 120 °C for 35 s after a 5 s ramp, the ashing temperature at 1100 °C for 10 s after a 30 s ramp, the cooling temperature at 800 °C for 5 s after a 5 s decrease, and the atomisation temperature at 2600 °C for 7 s. Use the zero solution to set the instrument to zero. Using the calibration curve, determine the concentrations of the test solution and the blank solution from the corresponding absorptions. If necessary, dilute with the zero solution to obtain a reading within the calibrated absorbance range.
Calculate the content of Ni in micrograms per gram (ppm) using the following expression:
| c | = | measured concentration of Ni, in nanograms per millilitre; |
| f | = | dilution factor of the test solution; |
| m | = | mass of the substance to be examined, in grams. |