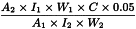Appendix VIII T. Methyl, Ethyl and Isopropyl Methanesulfonate in Active Substances
The following general method has been validated for the determination of methyl, ethyl and isopropyl esters of methanesulfonic acid (in concentrations between 0.2 ppm and 5 ppm) in betahistine mesilate.
If it is intended to use the method for other active substances, particularly those that contain different concentrations of the methanesulfonic acid esters, the concentrations of the test solution and reference solutions must be adjusted accordingly and the method must be suitably validated.
Method
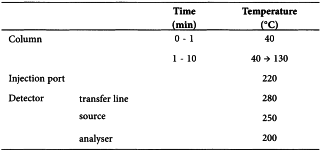
Head-space gas chromatography (2.2.28) coupled with mass spectrometry (2.2.43). Prepare the test solution and reference solutions immediately before use.
Solvent mixture water R, acetonitrile R (20:80 V/V). The use of acetonitrile of appropriate purity is essential.
Solution A Dissolve with the aid of ultrasound 30 mg of anhydrous sodium thiosulfate R and 60.0 g of sodium iodide R in water R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent.
Internal standard solution Dilute 10 µL of butyl methanesulfonate CRS (BMS) to 10.0 mL with the solvent mixture. Dilute 20 µL of the solution to 100.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Blank solution Introduce 0.50 mL of solution A and 0.50 mL of the internal standard solution into a headspace vial and seal the vial immediately with a polytetrafluoroethylene-coated silicon membrane and an aluminium cap.
Test solution Weigh 25.0 mg of the substance to be examined into a 20 mL headspace vial. Add 0.50 mL of solution A and 0.50 mL of the internal standard solution and seal the vial immediately with a polytetrafluoroethylene-coated silicon membrane and an aluminium cap.
Following the derivatisation reaction, a precipitate may be observed, however this does not affect the validity of the quantification.
Reference solution (a) Dissolve 25.0 mg each of methyl methanesulfonate R (MMS), ethyl methanesulfonate R (EMS) and isopropyl methanesulfonate R (IMS) in toluene R and dilute to 5.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 50 µL of the solution to 25.0 mL with the internal standard solution.
Reference solution (b) Dilute 20 µL of reference solution (a) to 20.0 mL with the internal standard solution. Introduce 0.50 mL of this solution and 0.50 mL of solution A into a 20 mL headspace vial and seal the vial immediately with a polytetrafluoroethylene-coated silicon membrane and an aluminium cap.
Reference solution (c) Dilute 500 µL of reference solution (a) to 20.0 mL with the internal standard solution. Introduce 0.50 mL of this solution and 0.50 mL of solution A into a 20 mL headspace vial and seal the vial immediately with a polytetrafluoroethylene-coated silicon membrane and an aluminium cap.
Carrier gas helium for chromatography R.
The use of an inert inlet liner without glass wool significantly reduces the effect of carry-over between the injections.
Flow rate 0.5 mL/min.
Split ratio 1:20.
At the end of analysis, the temperature of the column is raised to 240 °C and maintained at this temperature for 7 min.
Detection Mass spectrometer as described below; adjust the detector settings so as to comply with the system suitability criteria; alternatively a suitable electron-capture detector may be used:
Injection 1 mL of the gas phase of the test solution, reference solutions (b) and (c) and the blank solution.
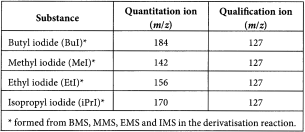
Relative retention With reference to the internal standard (BuI) (retention time = about 8.5 min): MeI = about 0.51; EtI = about 0.63; iPrI = about 0.68.
Calculate the content in parts per million of each alkyl methanesulfonate using the following expression:
| A1 | = | area of the peak due to each alkyl iodide in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c); |
| A2 | = | area of the peak due to each alkyl iodide in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution; |
| C | = | percentage content of each ester; |
| I1 | = | area of the peak due to the internal standard in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c); |
| I2 | = | area of the peak due to the internal standard in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution; |
| W1 | = | mass of each ester used to prepare reference solution (a), in milligrams; |
| W2 | = | mass of the substance to be examined in the test solution, in milligrams; |
| 0.05 | = | dilution factor. |