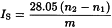Appendix X G. Saponification Value
The saponification value is the number of mg of potassium hydroxide required to neutralise the free acids and to saponify the esters in 1 g of the substance.
Use Method I unless otherwise specified in the monograph.
Method I
Dissolve 35 to 40 g of potassium hydroxide in 20 mL of water and add sufficient ethanol (96%) to produce 1000 mL. Allow to stand overnight and pour off the clear liquid.
Weigh 2 g of the substance into a 200-mL flask, add 25.0 mL of the ethanolic solution of potassium hydroxide and boil under a reflux condenser for 1 hour, rotating the contents frequently. While the solution is still hot, titrate the excess of alkali with 0.5m hydrochloric acid VS using 1 mL of phenolphthalein solution R1 as indicator. Repeat the operation without the substance being examined.
Calculate the saponification value from the expression 28.05 v/w where v is the difference, in mL, between the titrations and w is the weight, in g, of substance taken.
Method II
The saponification value IS is the number that expresses in milligrams the quantity of potassium hydroxide required to neutralise the free acids and to saponify the esters present in 1 g of the substance.
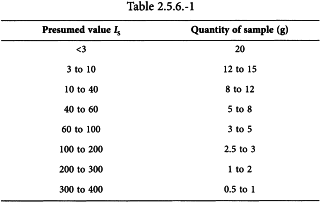
Unless otherwise prescribed, use the quantities indicated in Table 2.5.6.-1 for the determination.
Introduce the prescribed quantity of the substance to be examined (m g) into a 250 mL borosilicate glass flask fitted with a reflux condenser. Add 25.0 mL of 0.5 M alcoholic potassium hydroxide and a few glass beads. Attach the condenser and heat under reflux for 30 min, unless otherwise prescribed. Add 1 mL of phenolphthalein solution R1 and titrate immediately (while still hot) with 0.5 M hydrochloric acid (n1 mL of 0.5 M hydrochloric acid). Carry out a blank test under the same conditions (n2 mL of 0.5 M hydrochloric acid).