Appendix XI R. Test for Aristolochic Acids in Herbal Drugs
Use Method R1 unless otherwise directed in the monograph.
R1. Test for Aristolochic Acids in Herbal Drugs
CAUTION: aristolochic acids are very toxic and carcinogenic. Perform manipulations in a fume cupboard whenever possible. Take particular precautions, such as use of a glove box, when the substance is in dry form because of its electrostatic properties and the tendency to disperse through the working areas.
Methods A and B are intended to be cross-referenced in monographs on herbal drugs that, according to chemotaxonomic knowledge, are expected to be free from aristolochic acids, but that may be subject to adulteration or substitution with plant material containing aristolochic acids. Methods A and B are intended to be used in the screening of herbal drugs for aristolochic acids at the stated limits and will usually be complemented by macroscopic and/or microscopic tests to exclude plant material containing aristolochic acids.
Method C will not be used in specific monographs but is provided as a method to confirm the presence of aristolochic acid I at levels equal to or greater than 2 ppm. It may be applied if chromatographic data suggests the presence of aristolochic acid I.
These methods are not designed for inclusion as assay methods in monographs on those drugs that produce aristolochic acids as secondary metabolites; for these, a more sensitive, validated method is required.
Method A: screening test for aristolochic acids
Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Solvent mixtureanhydrous formic acid R, water R, methanol R (1:9:40 V/V/V).
Test solution To 1.0 g of the powdered herbal drug (710) (2.9.12) add 10.0 mL of the solvent mixture, sonicate for 10 min and centrifuge.
Reference solution (a) Disperse an amount of aristolochia HRS corresponding to 0.10 mg of aristolochic acid I in 20.0 mL of the solvent mixture, sonicate for 10 min and centrifuge.
Reference solution (b) Dilute 1.0 mL of reference solution (a) to 25.0 mL with methanol R.
PlateTLC silica gel F254 plate R (2-10 µm).
Mobile phaseanhydrous formic acid R, water R, ethyl acetate R, toluene R (3:3:30:60 V/V/V/V); use the upper layer.
Application 20 µL as bands of 8 mm.
Development Over a path of 6 cm.
Drying In a current of cold air for 5 min.
Detection Spray with a 100 g/L solution of stannous chloride R in dilute hydrochloric acid R until the plate is slightly wet, heat at 100 °C for 1 min and examine in ultraviolet light at 365 nm.
Results In the chromatogram obtained with the test solution no zone is similar in position and fluorescence to any of the zones due to aristolochic acids in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).
If the chromatogram obtained with the test solution shows any zones similar in position and fluorescence to any of the zones due to aristolochic acids I and II in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a), apply method B.
Method B: limit test for aristolochic acid I
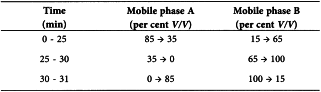
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Solvent mixtureacetonitrile R, water R (50:50 V/V).
Test solution Weigh 2.0 g of the powdered herbal drug (710) (2.9.12) into a 250 mL, brown, screw-cap bottle and add 100.0 mL of the solvent mixture. Stir for 30 min at about 300 r/min and filter through a membrane filter (nominal pore size 0.45 µm).
Reference solution (a) Dissolve the contents of a vial of aristolochic acid I CRS in the solvent mixture to obtain a concentration of 0.04 µg/mL of aristolochic acid I.
Reference solution (b) Dissolve the contents of a vial of aristolochic acid for system suitability CRS (containing aristolochic acids I and II) in the solvent mixture and dilute to 20.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Flow rate 0.3 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 390 nm.
Injection 25 µL.
Method C: confirmatory test for aristolochic acid i
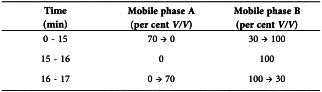
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29) coupled with mass spectrometry (2.2.43).
Solvent mixtureacetonitrile R, water R (50:50 V/V).
Test solution Weigh 2.0 g of the powdered herbal drug (710) (2.9.12) into a 250 mL, brown, screw-cap bottle and add 100.0 mL of the solvent mixture. Sonicate for 30 min and filter through a membrane filter (nominal pore size 0.45 µm).
Reference solution (a) Dissolve the contents of a vial of aristolochic acid I CRS in the solvent mixture to obtain a concentration of 0.04 µg/mL of aristolochic acid I.
Reference solution (b) Prepare a solution according to the instructions supplied with aristolochic acid I CRS to obtain a concentration of 0.45 µg of aristolochic acid I in 10.0 mL of the test solution.
Flow rate 0.4 mL/min.
Injection 20 µL; inject reference solution (a) twice, the test solution twice, reference solution (a) twice, then reference solution (b) twice.
Detection Mass detector as described below under A or B. Adjust the flow rate, the temperature and the detector settings so as to comply with the system suitability criterion.
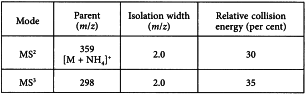
Set the mass spectrometer parameters for the MS3 mode as follows:
Results Evaluate the average ratios (252/268 and 281/268) of the relative intensity of the 3 product ions of aristolochic acid I in the test solution; evaluate the average of the 2 ratios of the signals at the retention time of aristolochic acid I in reference solution (a); if the average of the 2 ratios of the test solution is within the ± 40 per cent interval of the average of the 2 ratios of reference solution (a), aristolochic acid I is present in the test solution.
Set the mass spectrometer parameters for the MS2 mode as follows:
Results Evaluate the average ratios (265/281 and 296/281) of the relative intensity of the 3 product ions of aristolochic acid I in the test solution; evaluate the average of the 2 ratios of the signals at the retention time of aristolochic acid I in reference solution (a); if the average of the 2 ratios of the test solution is within the ± 40 per cent interval of the average of the 2 ratios of reference solution (a), aristolochic acid I is present in the test solution.
R2. Test for Aristolochic Acids I and II in Herbal Drugs
cautionAristolochic acids have been shown to be highly toxic and carcinogenic. Extraordinary care should be taken in any procedure in which they are used.
In line with the prohibition of the use of Aristolochia species in unlicensed herbal medicines in the United Kingdom, a test for absence of aristolochic acids I and II in herbal drugs has been included in the British Pharmacopoeia. The limit of detection has been shown to be 0.00078 mg/mL (approximately 1 ppm of aristolochic acids I and II). It is advised that the limit of detection for the system-in-use is determined by the analyst. Aristolochic acids I and II are not confined to the genus Aristolochia. The acids are also reported as present in certain species of Asarum.
Sample preparation
Unless otherwise specified in the monograph, weigh 2 g of the ground herbal drug into a centrifuge tube. Add 10 mL of 0.1m sodium hydroxide, shake for at least 2 hours and centrifuge the mixture for 10 minutes at approximately 4000 revolutions per minute. Filter the supernatant layer if visible particles remain in the suspension. Pass a 1.0 mL portion of the sample solution with the aid of vacuum through a solid-phase extraction column of 1 mL capacity and containing 30 mg of divinylbenzene and vinylpyrrolidone copolymer for chromatography (30 µm) (Waters Oasis HLB, 30 mg/mL or Phenomenex StrataX, 30 mg/mL is suitable) previously washed with 1 mL of methanol, followed by 1 mL of water. Wash the column with 1 mL of 0.1m sodium hydroxide followed by 1 mL of a mixture containing 2 volumes of glacial acetic acid, 28 volumes of water and 70 volumes of methanol. Elute the sample with 0.25 mL of a mixture containing 98% of methanol and 2% of concentrated ammonia. Evaporate the extract to dryness at 40° under a stream of nitrogen and dissolve in 0.25 mL of methanol. If a larger sample volume is required then a larger capacity solid-phase extraction column may be used.
Use this as solution (1) for the identification method described below.
Identification
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, using the following solutions. Prepare solution (1) as described above under Sample preparation. Solution (2) contains 0.01% w/v of aristolochic acid BPCRS in methanol.
The chromatographic procedure may be carried out using (a) a stainless steel column (25 cm × 4.6 mm) packed with base-deactivated octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography (4 µm) (Genesis C18 is suitable) maintaining the column temperature at 30°, (b) a mixture of 45 volumes of 0.1% v/v of orthophosphoric acid and 55 volumes of acetonitrile as the mobile phase with a flow rate of 1.3 mL per minute and (c) a detection wavelength of 225 nm. The identity of any peaks suspected to be due to arisotolochic acids I and II may be clarified by use of the UV spectrum recorded with a diode array detector.
Inject 10 µL of solution (2) and allow the chromatography to proceed for 10 minutes. The test is not valid unless the resolution factor between the peaks corresponding to aristolochic acid II (retention time about 6 minutes) and aristolochic acid I (retention time about 7 minutes) is at least 3.0. Inject solution (2) six times. The relative standard deviation of the areas of the peaks is at most 1.5%.
Inject 10 µL of solution (1) and allow the chromatography to proceed for 30 minutes. In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) the peaks due to aristolochic acid I and aristolochic acid II are absent.