Appendix XVI F. Microbiological Examination of Herbal Medicinal Products for Oral Use and Extracts used in their Preparation
1 MICROBIAL ENUMERATION TESTS
Total aerobic microbial count (TAMC)
Perform as described in general chapter 2.6.12.
Total combined yeasts/moulds count (TYMC)
Perform as described in general chapter 2.6.12. Due to the natural high bioburden in the products covered by general chapter 5.1.8, use of Sabouraud-dextrose agar containing antibiotics is suitable.
2 TEST FOR SPECIFIED MICRO-ORGANISMS
2-1 INTRODUCTION
The tests described hereafter will allow determination of the absence or limited occurrence of specified micro-organisms that may be detected under the conditions described.
The tests are designed primarily to determine whether a product, substance or preparation (hereinafter referred to as ‘the product’) complies with an established specification for microbiological quality. When used for such purposes, follow the instructions given below, including the number of samples to be taken, and interpret the results as stated below.
Alternative microbiological procedures, including automated methods, may be used, provided that their equivalence to the Pharmacopoeia method has been demonstrated.
2-2 General procEdures
The preparation of samples is carried out as described in general chapter 2.6.12.
If the product to be examined has antimicrobial activity, this is as far as possible removed or neutralised as described in general chapter 2.6.12.
If surface-active substances are used for sample preparation, their absence of toxicity for micro-organisms and their compatibility with inactivators used must be demonstrated as described in general chapter 2.6.12.
2-3 Growth-promoting and inhibitory properties of the media, suitability of the test AND NEGATIVE CONTROLS
The ability of the test to detect micro-organisms in the presence of the product to be examined must be established. Suitability must be confirmed if a change in testing performance, or the product, which may affect the outcome of the test is introduced.
2-3-1 Preparation of test strains
Use standardised stable suspensions of test strains or prepare them as stated below. Seed lot culture maintenance techniques (seed-lot systems) are used so that the viable micro-organisms used for inoculation are not more than 5 passages removed from the original master seed lot.
2-3-1-1 Aerobic micro-organisms
Grow each of the bacterial test strains separately in casein soya bean digest broth or on casein soya bean digest agar at 30-35 °C for 18-24 h.
Use buffered sodium chloride-peptone solution pH 7.0 or phosphate buffer solution pH 7.2 to make test suspensions. Use the suspensions within 2 h, or within 24 h if stored at 2-8 °C. As an alternative to preparing and then diluting a fresh suspension of vegetative cells of B. subtilis, a stable spore suspension is prepared and then an appropriate volume is used for test inoculation. The stable spore suspension may be maintained at 2-8 °C for a validated period of time.
2-3-2 Negative control
To verify testing conditions, a negative control is performed using the chosen diluent in place of the test preparation. There must be no growth of micro-organisms. A negative control is also performed when testing the products as described in section 2-4. A failed negative control requires an investigation.
2-3-3 Growth-promoting and inhibitory properties of the media
Test each batch of ready-prepared medium and each batch of medium prepared either from dehydrated medium or from the ingredients described.
Verify suitable properties of relevant media as described in Table 2.6.31.-1.
Test for growth-promoting properties, liquid media
Inoculate a portion of the appropriate medium with a small number (not more than 100 CFU) of the appropriate micro-organism. Incubate at the specified temperature for not more than the shortest period of time specified in the test. Incubate the casein soya bean digest broth at 30-35 °C for not more than 3 days. Clearly visible growth of the micro-organism comparable to that obtained with a previously tested and approved batch of medium occurs.
Test for growth-promoting properties, solid media
Perform the surface-spread method, inoculating each plate with a small number (not more than 100 CFU) of the appropriate micro-organism. Incubate at the specified temperature for not more than the shortest period of time specified in the test. Growth of the micro-organism comparable to that obtained with a previously tested and approved batch of medium occurs.
Test for inhibitory properties, liquid or solid media
Inoculate the appropriate medium with at least 100 CFU of the appropriate micro-organism. Incubate at the specified temperature for not less than the longest period of time specified in the test. No growth of the test micro-organism occurs.
Test for indicative properties
Perform the surface-spread method, inoculating each plate with a small number (not more than 100 CFU) of the appropriate micro-organism. Incubate at the specified temperature for a period of time within the range specified in the test. Colonies are comparable in appearance and indication reactions to those obtained with a previously tested and approved batch of medium.
2-3-4 Suitability of the test method
For each product to be examined, perform the sample preparation as described in the relevant paragraph in section 2-4. Add each test strain at the time of mixing, in the prescribed growth medium (casein soya bean digest broth or buffered peptone medium). For the enumeration method for bile-tolerant gram-negative bacteria, inoculate E. coli and P. aeruginosa individually. For the tests for E. coli and Salmonella, inoculate the specified micro-organism individually.
Any antimicrobial activity of the product necessitates a modification of the test procedure (see section 4-5-3 of general chapter 2.6.12).
If for a given product the antimicrobial activity with respect to a micro-organism for which testing is prescribed cannot be neutralised, then it is to be assumed that the inhibited micro-organism will not be present in the product.
2-3-4-1 Test for absence
Use a number of micro-organisms equivalent to not more than 100 CFU in the inoculated test preparation. Perform the test as described in the relevant paragraph in section 2-4 using the shortest incubation period prescribed. The specified micro-organisms must be detected with the indication reactions as described in section 2-4.
2-3-4-2 Enumeration test
Semi-quantitative test (probable-number method).
Use a number of micro-organisms equivalent to not more than 100 CFU per gram or millilitre of product. Perform the test as described in the relevant paragraph in section 2-4 using the shortest incubation period prescribed. The dilution corresponding to 0.1 g or 0.1 mL of product must be positive.
2-4 TESTING OF PRODUCTS
2-4-1 Bile tolerant gram negative bacteria
2-4-1-1 Enumeration test
Semi-quantitative test (probable-number method).
2-4-1-1-1 Sample preparation and pre-incubation Prepare a sample using a 10-fold dilution of not less than 1 g of the product to be examined as described in general chapter 2.6.12, but using casein soya bean digest broth as the chosen diluent, mix and incubate at 20-25 °C for a time sufficient to resuscitate the bacteria but not sufficient to encourage multiplication of the organisms (2-3 h).
2-4-1-1-2 Selection and subculture Inoculate suitable quantities of enterobacteria enrichment broth-Mossel with the preparation as described above and/or, depending on the limit applied for the particular product, with 3 of the 4 dilutions of the preparation, which contain respectively 0.1 g, 0.01 g, 0.001 g and 0.0001 g (or 0.1 mL, 0.01 mL, 0.001 mL and 0.0001 mL) of the product to be examined. Incubate at 30-35 °C for 24-48 h. Subculture each of the cultures on a plate of violet red bile glucose agar. Incubate at 30-35 °C for 18-24 h.
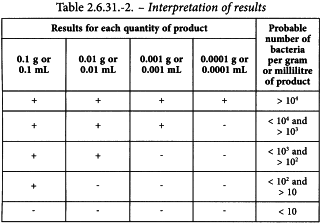
2-4-1-1-3 Interpretation. Growth of colonies constitutes a positive result. Note the smallest quantity of the product that gives a positive result and the largest quantity that gives a negative result.
Determine from Table 2.6.31.-2 the probable number of bacteria.
2-4-2 Escherichia coli
2-4-2-1 Test for absence
2-4-2-1-1 Sample preparation and pre-incubation Prepare a sample using a 10-fold dilution of not less than 1 g of the product to be examined as described in general chapter 2.6.12, and use 10 mL or the quantity corresponding to 1 g or 1 mL to inoculate a suitable amount (determined as described in section 2-3-4) of casein soya bean digest broth, mix and incubate at 30-35 °C for 18-24 h.
2-4-2-1-2 Selection and subculture Shake the container, transfer 1 mL of casein soya bean digest broth to 100 mL of MacConkey broth and incubate at 42-44 °C for 24-48 h. Subculture on a plate of MacConkey agar at 30-35 °C for 18-72 h.
2-4-2-1-3 Interpretation Growth of colonies indicates the possible presence of E. coli. This is confirmed by identification tests.
The product complies with the test if no colonies are present or if the identification tests are negative.
2-4-2-2 Enumeration test
Semi-quantitative test (probable-number method).
2-4-2-2-1 Sample preparation and pre-incubation Prepare a sample using a 10-fold dilution of not less than 1 g of the product to be examined as described in general chapter 2.6.12, and use the quantities corresponding respectively to 0.1 g, 0.01 g and 0.001 g (or 0.1 mL, 0.01 mL and 0.001 mL) to inoculate a suitable amount (determined as described in section 2-3-4) of casein soya bean digest broth, mix and incubate at 30-35 °C for 18-24 h.
2-4-2-2-2 Selection and subculture Shake the container, transfer 1 mL of casein soya bean digest broth to 100 mL of MacConkey broth and incubate at 42-44 °C for 24-48 h. Subculture on a plate of MacConkey agar at 30-35 °C for 18-72 h.
2-4-2-2-3 Interpretation Growth of colonies indicates the possible presence of E. coli. This is confirmed by identification tests.
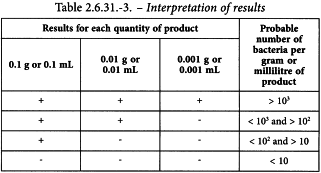
Note the smallest quantity of the product that gives a positive result and the largest quantity that gives a negative result.
Determine from Table 2.6.31.-3 the probable number of bacteria.
2-4-3 Salmonella
2-4-3-1 Test for absence
2-4-3-1-1 Sample preparation and pre-incubation. Use 25 g or 25 mL of the product to be examined to inoculate 225 mL of buffered peptone medium and mix (e.g. homogenise in a filter bag by using a blender). Incubate at 30-35 °C for 18-24 h.
2-4-3-1-2 Selection and subculture. Transfer 0.1 mL of buffered peptone medium to 10 mL of Rappaport Vassiliadis Salmonella enrichment broth and incubate at 30-35 °C for 18-24 h. Subculture on plates of xylose, lysine and deoxycholate agar. Incubate at 30-35 °C for 18-48 h.
2-4-3-1-3 Interpretation. The possible presence of Salmonella is indicated by the growth of well-developed, red colonies, with or without black centres. This is confirmed by identification tests.
The product complies with the test if colonies of the types described are not present or if the identification tests are negative.
The following section is given for information.
RECOMMENDED SOLUTIONS AND CULTURE MEDIA
The solutions and culture media mentioned in this chapter and described in general chapter 2.6.13 and the following buffered peptone medium have been found to be satisfactory for the purposes for which they are prescribed in this chapter. Other media may be used provided that their suitability can be demonstrated.
Adjust the pH so that after sterilisation it is 7.0 ± 0.2 at 25 °C. Sterilise in an autoclave using a validated cycle.