Action and use
Penicillin antibacterial.
Definition
Ampicillin Capsules contain Ampicillin or Ampicillin Trihydrate.
The capsules comply with the requirements stated under Capsules and with the following requirements.
Content of ampicillin, C16H19N3O4S
92.5 to 107.5% of the stated amount.
Identification
(1) Shake a quantity of the capsule contents containing the equivalent of 0.125 g of ampicillin with sufficient
sodium hydrogen carbonate solution to produce 50 mL and filter.
chromatographic conditions
(b) Use the mobile phase described below.
(c) Apply 1 µL of each solution.
(d) Develop the plate to 15 cm.
(e) After removal of the plate, allow it to dry in air, expose it to iodine vapour until spots appear and examine in daylight.
mobile phase
10 volumes of acetone and 90 volumes of a 15.4% w/v solution of ammonium acetate adjusted to pH 5.0 with glacial acetic acid.
system suitability
The test is not valid unless the chromatogram obtained with solution (3) shows two clearly separated spots.
confirmation
The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) is similar in position, colour and size to that in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2).
B. Suspend a quantity of the capsule contents containing the equivalent of 10 mg of ampicillin in 1 mL of
water and add 2 mL of a mixture of 2 mL of
cupri-tartaric solution R1 and 6 mL of
water. A magenta-violet colour is produced immediately.
Tests
Related substances
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, using the following solutions.
(1) Shake a quantity of the mixed capsule contents containing the equivalent of 0.3 g of ampicillin with 80 mL of mobile phase A with the aid of ultrasound for 15 minutes, add sufficient mobile phase A to produce 100 mL and filter through a 0.4-µm filter.
(2) Dilute 1 volume of solution (1) to 100 volumes with mobile phase A.
chromatographic conditions
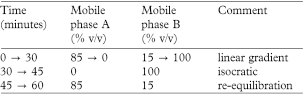
(b) Use gradient elution and the mobile phase described below. Equilibrate the column with a mobile phase ratio A:B of 85:15 and use this for the system suitability solution (3). Inject solutions (1) and (2) and start the elution isocratically with the chosen mobile phase. Immediately after elution of the ampicillin peak start the linear gradient elution.
(c) Use a flow rate of 1 mL per minute.
(d) Use an ambient column temperature.
(e) Use a detection wavelength of 254 nm.
(f) Inject 50 µL of each solution.
mobile phase
Inject mobile phase A and use the same elution gradient to obtain a blank.
system suitability
The test is not valid unless, in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3), the resolution factor between the peaks due to ampicillin and cefradine is at least 3.0. If necessary, adjust the composition of the mobile phase.
limits
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1):
the area of any secondary peak is not greater than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (1%).
Assay
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, using the following solutions.
(1) Shake a quantity of the mixed contents of 20 capsules containing the equivalent of 60 mg of ampicillin with 80 mL of solution A for 15 minutes, dilute to 100 mL with the same solvent, filter and dilute 5 mL of the solution to 50 mL with solution A.
chromatographic conditions
(b) Use isocratic elution and the mobile phase described below.
(c) Use a flow rate of 1 mL per minute.
(d) Use an ambient column temperature.
(e) Use a detection wavelength of 254 nm.
(f) Inject 50 µL of each solution.
mobile phase
15 volumes of solution B and 85 volumes of solution A.
system suitability
The assay is not valid unless, in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3), the resolution factor between the peaks due to ampicillin and cefradine is at least 3.0. If necessary, adjust the composition of the mobile phase to achieve the required resolution.
determination of content
Calculate the content of C16H19N3O4S in the capsules using the declared content of C16H19N3O4S in anhydrous ampicillin BPCRS.
Labelling
When the active ingredient is Ampicillin Trihydrate, the quantity is stated in terms of the equivalent amount of ampicillin.