Indapamide Tablets
Action and use
Thiazide-like diuretic.
Definition
Indapamide Tablets contain Indapamide. They are coated.
Production
A suitable test is carried out to demonstrate that the content of (2RS)-2-methyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-1-amine (impurity C) is not more than 600 ppm.
Content of indapamide hemihydrate, C16H16ClN3O3S,½H2O
95.0 to 105.0% of the stated amount.
Identification
A. Carry out the method for thin-layer chromatography, Appendix III A, using the following solutions.
20 volumes of acetone and 80 volumes of toluene
By each method of visualisation, the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) is similar in position, colour and intensity to that in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2).
Tests
Dissolution
Comply with the requirements for Monographs of the British Pharmacopoeia in the dissolution test for tablets and capsules, Appendix XII B1.
Calculate the total content of indapamide hemihydrate, C16H16ClN3O3S,½H2O, in the medium using the differences in absorbance at 240 nm and at 275 nm and using the declared content of C16H16ClN3O3S in indapamide BPCRS.Each mg of C16H16ClN3O3S is equivalent to 1.0246 mg of C16H16ClN3O3S,½H2O. The amount of indapamide hemihydrate released is not less than 75% of the stated amount.
Related substances
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, protected from light, using the following solutions.
6 volumes of a solution containing 5% w/v of sodium dodecyl sulfate and 3% v/v of glacial acetic acid, 10 volumes of triethylamine, 20 volumes of butan-2-ol, 310 volumes of acetonitrile and 690 volumes of water, the mixture being adjusted to pH 3.0 with orthophosphoric acid.
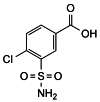
The test is not valid unless, in the chromatogram obtained with solution (5), the retention of impurity B relative to indapamide is about 1.7 and the retention of 4-chloro-3-sulfamoylbenzoic acid relative to indapamide is about 0.3.
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1):
the area of any peak corresponding to impurity B is not greater than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3) (0.5%);
the area of any peak corresponding to 4-chloro-3-sulfamoylbenzoic acid is not greater than 0.4 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (4) (0.2%);
the area of any other secondary peak is not greater than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.1%).
The sum of the impurities, excluding impurity B, is not greater than 0.3%.
Disregard any peak with an area less than half the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.05%).
Assay
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, protected from light, using the following solutions.
The chromatographic procedure described under Related substances may be used.
Calculate the content of C16H16ClN3O3S,½H2O in the tablets from the chromatogram obtained using the declared content of C16H16ClN3O3S in indapamide BPCRS. Each mg of C16H16ClN3O3S is equivalent to 1.0246 mg of C16H16ClN3O3S,½H2O.
Storage
Indapamide Tablets should be protected from light.
IMPURITIES
The impurities limited by the requirements of this monograph include impurities B and C listed under Indapamide and the following: