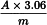Standardised Frangula Bark Dry Extract
Ph Eur
DEFINITION
Standardised dry extract obtained from Frangula bark (0025).
Content
15.0 per cent to 30.0 per cent of glucofrangulins, expressed as glucofrangulin A (C27H30O14; Mr 578.5) (dried extract). The measured content does not deviate from that stated on the label by more than ± 10 per cent.
PRODUCTION
The extract is produced from the herbal drug by a suitable procedure using ethanol (50-90 per cent V/V).
CHARACTERS
Appearance
Yellowish-brown, fine powder.
IDENTIFICATION
Test solution To 0.05 g of the extract to be examined add 5 mL of ethanol (70 per cent V/V) R and heat to boiling. Cool and centrifuge. Decant the supernatant immediately and use within 30 min.
Reference solution Dissolve 20 mg of barbaloin R in ethanol (70 per cent V/V) R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
PlateTLC silica gel plate R.
Mobile phasewater R, methanol R, ethyl acetate R (13:17:100 V/V/V).
Application 10 µL as bands.
Development Over a path of 10 cm.
Drying In air for 5 min.
Detection Treat with a 50 g/L solution of potassium hydroxide R in ethanol (50 per cent V/V) R and heat at 100-105 °C for 15 min; examine immediately after heating.
Results The chromatogram obtained with the reference solution shows in the middle third a reddish-brown zone due to barbaloin. The chromatogram obtained with the test solution shows 2 orange-brown zones (glucofrangulins) in the lower third and 2-4 red zones (frangulins, not always clearly separated, and above them frangula-emodin) in the upper third.
TESTS
Loss on drying (2.8.17)
Maximum 5.0 per cent.
ASSAY
Carry out the assay protected from bright light.
Into a tared round-bottomed flask with a ground-glass neck, weigh 0.100 g. Add 25.0 mL of a 70 per cent V/V solution of methanol R, mix and weigh again. Heat the flask in a water-bath under a reflux condenser at 70 °C for 15 min. Allow to cool, weigh and adjust to the original mass with a 70 per cent V/V solution of methanol R. Filter and transfer 5.0 mL of the filtrate to a separating funnel. Add 50 mL of water R and 0.1 mL of hydrochloric acid R. Shake with 5 quantities, each of 20 mL, of light petroleum R1. Allow the layers to separate and transfer the aqueous layer to a 100 mL volumetric flask. Combine the light petroleum layers and wash with 2 quantities, each of 15 mL, of water R. Use this water for washing the separating funnel and add it to the aqueous solution in the volumetric flask. Add 5 mL of a 50 g/L solution of sodium carbonate R and dilute to 100.0 mL with water R. Discard the light petroleum layer. Transfer 40.0 mL of the aqueous solution to a 200 mL round-bottomed flask with a ground-glass neck. Add 20 mL of a 200 g/L solution of ferric chloride R and heat under a reflux condenser for 20 min in a water-bath with the water level above that of the liquid in the flask. Add 2 mL of hydrochloric acid R and continue heating for 20 min, shaking frequently, until the precipitate is dissolved. Allow to cool, transfer the mixture to a separating funnel and shake with 3 quantities, each of 25 mL, of ether R, previously used to rinse the flask. Combine the ether extracts and wash with 2 quantities, each of 15 mL, of water R. Transfer the ether layer to a volumetric flask and dilute to 100.0 mL with ether R. Evaporate 20.0 mL carefully to dryness and dissolve the residue in 10.0 mL of a 5 g/L solution of magnesium acetate R in methanol R. Measure the absorbance (2.2.25) at 515 nm using methanol R as the compensation liquid.
Calculate the percentage content of glucofrangulins, expressed as glucofrangulin A, using the following expression:
i.e. taking the specific absorbance of glucofrangulin A to be 204, calculated on the basis of the specific absorbance of barbaloin.
A | = | absorbance at 515 nm; |
m | = | mass of the extract to be examined, in grams. |
LABELLING
The label states the content of glucofrangulins.
Ph Eur