 Apo-Perphenazine, Phenazine, PMS-Perphenazine
Apo-Perphenazine, Phenazine, PMS-PerphenazinePerphenazine
A to Z Drug Facts
| Perphenazine |
| (per-FEN-uh-zeen) |
Trilafon,  Apo-Perphenazine, Phenazine, PMS-Perphenazine Apo-Perphenazine, Phenazine, PMS-Perphenazine |
| Class: Antipsychotic/Phenothiazine/Antiemetic |
 Action Effects apparently caused by postsynaptic dopamine receptor blockade in CNS.
Action Effects apparently caused by postsynaptic dopamine receptor blockade in CNS.
 Indications Management of psychotic disorders; control of severe nausea/vomiting; intractable hiccoughs in adults. Unlabeled use(s): Treatment of Tourette's syndrome; control of acute agitation in elderly; useful in controlling some symptoms of dementia such as agitation, hyperactivity, hallucinations, suspiciousness, hostility and uncooperative behaviors; treatment of hemiballismus (violent writhing/movement of one side of body).
Indications Management of psychotic disorders; control of severe nausea/vomiting; intractable hiccoughs in adults. Unlabeled use(s): Treatment of Tourette's syndrome; control of acute agitation in elderly; useful in controlling some symptoms of dementia such as agitation, hyperactivity, hallucinations, suspiciousness, hostility and uncooperative behaviors; treatment of hemiballismus (violent writhing/movement of one side of body).
 Contraindications Comatose or severely depressed states; allergy to any phenothiazine; presence of large amounts of other CNS depressants; bone marrow depression or blood dyscrasias; liver damage; subcortical brain damage.
Contraindications Comatose or severely depressed states; allergy to any phenothiazine; presence of large amounts of other CNS depressants; bone marrow depression or blood dyscrasias; liver damage; subcortical brain damage.
Psychiatric
ADULT: Nonhospitalized patients: PO 4 to 8 mg tid, reduce as soon as possible to minimum effective dosage.
Hospitalized patients: PO 8 to 16 mg bid to qid; avoid dosages > 64 mg/day.
Nausea/Vomiting/Hiccoughs
ADULTS: PO 8–16 mg/day in divided doses. (Give elderly and debilitated patients lower doses. Administer 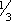 to ½ adult dose.) CHILDREN > 12 YR May be given lowest limit of adult dosage.
to ½ adult dose.) CHILDREN > 12 YR May be given lowest limit of adult dosage.
IM
Doses range from 5 to 10 mg/injection, usually given q 6 hr. Do not exceed 30 mg/day. Administer by deep injection to seated or recumbent patient. IM administration usually reserved for instances in which patient is unwilling or unable to take oral medication.
ORAL LIQUID CONCENTRATE AND IV FORM
Alcohol: May result in increased CNS depression and may precipitate extrapyramidal reaction. Anticholinergics: May reduce therapeutic effects of perphenazine and worsen anticholinergic effects. Concomitant administration may worsen schizophrenic symptoms and lead to tardive dyskinesia (see Precautions). Barbiturate anesthetics: Frequency and severity of neuromuscular excitation and hypotension may increase. Guanethidine: Hypotensive action of guanethidine may be inhibited. Metrizamide: Possibility of seizure may be increased when subarachnoid metrizamide injection is used.
 Lab Test Interferences May discolor urine pink to red-brown. False-positive pregnancy tests may occur but are less likely to occur with serum test. Increases in protein-bound iodine have been reported.
Lab Test Interferences May discolor urine pink to red-brown. False-positive pregnancy tests may occur but are less likely to occur with serum test. Increases in protein-bound iodine have been reported.
CV: Orthostatic hypotension; hypertension; tachycardia; bradycardia; syncope; cardiac arrest; circulatory collapse; lightheadedness; faintness; dizziness; ECG changes. CNS: Pseudoparkinsonism dystonia; dyskinesia, motor restlessness; oculogyric crisis; dystonias; hyperreflexia; tardive dyskinesia; drowsiness; headache; fatigue; abnormalities of the cerebrospinal fluid proteins; paradoxical excitement or exacerbation of psychotic symptoms; catatonic-like states; weakness; tremor; paranoid reactions; lethargy; seizures; hyperactivity; nocturnal confusion; bizarre dreams; vertigo; insomnia. DERM: Photosensitivity; skin pigmentation; dry skin; exfoliative dermatitis; urticarial rash; maculopapular hypersensitivity reaction; seborrhea; eczema. EENT: Pigmentary retinopathy; glaucoma; photophobia; blurred vision; mydriasis; increased intraocular pressure; dry mouth or throat; nasal congestion. GI: Dyspepsia; adynamic ileus (may result in death); nausea; vomiting; constipation. GU: Urinary hesitancy or retention; impotence; sexual dysfunction; menstrual irregularities. HEMA: Agranulocytosis; eosinophilia; leukopenia; hemolytic anemia; thrombocytopenic purpura. HEPA: Jaundice. META: Hyperglycemia; hypoglycemia; decreased cholesterol. RESP: Laryngospasm; bronchospasm; dyspnea. OTHER: Increases in appetite and weight; polydipsia; breast enlargement; galactorrhea; increased prolactin levels.
Pregnancy: Pregnancy category undetermined. Lactation: Undetermined. Children: Not recommended in children < 12 yr. Elderly: More susceptible to effects; consider lower dose. Special-risk patients: Use caution in patients with cardiovascular disease or mitral insufficiency, history of glaucoma, EEG abnormalities or seizure disorders, prior brain damage, hepatic or renal impairment. Antiemetic effects: Because of suppression of cough reflex, aspiration of vomitus possible. CNS effects: May impair mental or physical abilities, especially during first few days of therapy. Hepatic effects: Jaundice usually occurs between second and fourth weeks of treatment; considered hypersensitivity reaction. Usually reversible. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome: Has occurred with agents of this class; is potentially fatal. Signs and symptoms are hyperpyrexia, muscle rigidity, altered mental status, irregular pulse, irregular blood pressure, tachycardia, and diaphoresis. Pulmonary: Cases of bronchopneumonia, some fatal, have occurred. Sudden death: Has been reported; predisposing factors may be seizures or previous brain damage. Flare-ups of psychotic behavior may precede death. Tardive dyskinesia: Syndrome of potentially irreversible involuntary body and facial movements may develop. Prevalence highest in elderly, especially women. Use smallest effective doses for shortest possible time period.
| PATIENT CARE CONSIDERATIONS |
|
Oral Liquid Concentrate
IV
IM
|
||||
Books@Ovid
Copyright © 2003 Facts and Comparisons
David S. Tatro
A to Z Drug Facts