Appendix XVI D. Microbiological Quality of Non-sterile Pharmaceutical Preparations and Substances for Pharmaceutical Use1
The presence of certain micro-organisms in non-sterile preparations may have the potential to reduce or even inactivate the therapeutic activity of the product and has a potential to adversely affect the health of the patient. Manufacturers therefore have to ensure a low bioburden of finished dosage forms by implementing current guidelines on Good Manufacturing Practice during the manufacture, storage and distribution of pharmaceutical preparations.
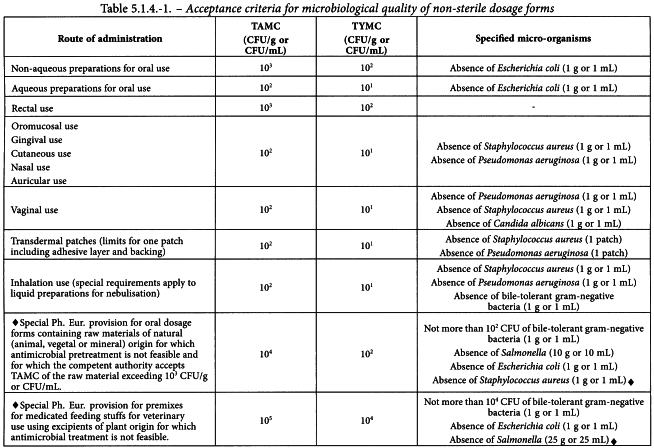
Microbial examination of non-sterile products is performed according to the methods given in general chapters 2.6.12 and 2.6.13. Acceptance criteria for non-sterile pharmaceutical products based upon the total aerobic microbial count(TAMC) and the total combined yeasts/moulds count (TYMC) are given in Tables 5.1.4.-1 and 5.1.4.-2. Acceptance criteria are based on individual results or on the average of replicate counts when replicate counts are performed (e.g. direct plating methods).
When an acceptance criterion for microbiological quality is prescribed it is interpreted as follows:
Table 5.1.4.-1 includes a list of specified micro-organisms for which acceptance criteria are set. The list is not necessarily exhaustive and for a given preparation it may be necessary to test for other micro-organisms depending on the nature of the starting materials and the manufacturing process.
If it has been shown that none of the prescribed tests will allow valid enumeration of micro-organisms at the level prescribed, a validated method with a limit of detection as close as possible to the indicated acceptance criterion is used.
In addition to the micro-organisms listed in Table 5.1.4.-1, the significance of other micro-organisms recovered is evaluated in terms of:
Where warranted, a risk-based assessment of the relevant factors is conducted by personnel with specialised training in microbiology and the interpretation of microbiological data. For raw materials, the assessment takes account of processing to which the product is subjected, the current technology of testing and the availability of materials of the desired quality.
♦Recommended acceptance criteria for microbiological quality of herbal medicinal products for oral use and extracts used in their preparation are given in general chapter 5.1.8.♦