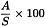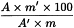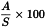Appendix X Q. Sterols in Fatty Oils
Method A
Separation of the sterol fraction (TLC)
Prepare the unsaponifiable matter and then isolate the sterol fraction of the fatty oil by thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27), using a TLC silica gel plate R with a 0.2 mm to 0.5 mm layer.
Test solution (a) In a 150 mL flask fitted with a reflux condenser, place a volume of a 2 g/L solution of betulin R in methylene chloride R containing betulin corresponding to about 10 per cent of the sterol content of the sample used for the determination (e.g. in the case of olive oil add 500 µL, in the case of other vegetable oils add 1500 µL of the betulin solution). If the monograph requires the percentage content of the individual sterols in the sterol fraction, the addition of betulin may be omitted. Evaporate to dryness under a current of nitrogen R. Add 5.00 g (m) of the substance to be examined. Add 50 mL of 2 M alcoholic potassium hydroxide R and heat on a water-bath for 1 h, swirling frequently. Cool to a temperature below 25 °C and transfer the contents of the flask to a separating funnel with 100 mL of water R. Shake the liquid carefully with 3 quantities, each of 100 mL, of peroxide-free ether R. Combine the ether layers in another separating funnel containing 40 mL of water R, shake gently for a few minutes, allow to separate and reject the aqueous phase. Wash the ether phase with several quantities, each of 40 mL, of water R, until the aqueous phase is no longer alkaline to phenolphthalein. Transfer the ether phase to a tared flask, washing the separating funnel with peroxide-free ether R. Distil off the ether with suitable precautions and add 6 mL of acetone R to the residue. Carefully remove the solvent in a current of nitrogen R. Dry to constant mass at 100-105 °C. Allow to cool in a desiccator and weigh. Transfer the residue to a small test tube with methylene chloride R. Evaporate under a stream of nitrogen R to a volume of about 1 mL. Depending on the unsaponifiable content of the oil, adapt the final concentration of the solution to 25-50 mg/mL.
Test solution (b) Treat 5.00 g of rapeseed oil R as prescribed for the substance to be examined, beginning at the words “Add 50 mL of 2 M alcoholic potassium hydroxide R”.
Test solution (c) Treat 5.00 g of sunflower oil R as prescribed for the substance to be examined, beginning at the words “Add 50 mL of 2 M alcoholic potassium hydroxide R”.
Reference solution Dissolve 25 mg of cholesterol R and 10 mg of betulin R in 1 mL of methylene chloride R.
Use a separate plate for each test solution. Apply as a band of 10 mm, at 20 mm from the base and 10 mm from the left edge, 10 µL of the reference solution and as bands of 150 mm, at 20 mm from the base, 0.5 mL of test solutions (a), (b) or (c). Develop over a path of 17 cm using a mixture of 35 volumes of ether R and 65 volumes of hexane R. Dry the plates in a current of nitrogen R. Spray the plates with a 2 g/L solution of dichlorofluorescein R in anhydrous ethanol R and examine in ultraviolet light at 254 nm. The chromatogram obtained with the reference solution shows bands due to cholesterol and betulin. The chromatograms obtained with the test solutions show bands with similar RF values due to sterols. From each of the chromatograms, remove an area of coating corresponding to the area occupied by the sterol bands and additionally the area of the zones 2-3 mm above and below the visible zones corresponding to the reference solution. Place separately in three 50 mL flasks. To each flask add 15 mL of methylene chloride R and heat under reflux with stirring, for 15 min. Filter each solution through a sintered-glass filter (40) (2.1.2) or suitable filter paper and wash each filter with 3 quantities, each of 15 mL, of methylene chloride R. Place the combined filtrate and washings from each filter separately in 3 flasks, evaporate under a stream of nitrogen R to 5-10 mL. Transfer to a small test tube and evaporate to dryness under a stream of nitrogen R.
Determination of the sterols (GC)
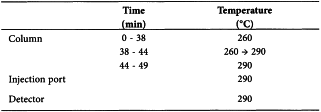
Gas chromatography (2.2.28). Carry out the operations protected from humidity and prepare the solutions immediately before use.
Test solution To the sterols separated from the substance to be examined by thin-layer chromatography add a freshly prepared mixture of 0.04 mL of chlorotrimethylsilane R, 0.1 mL of hexamethyldisilazane R and 0.5 mL of anhydrous pyridine R. Allow to stand for at least 5 min and use the liquid phase.
Reference solution (a) To 9 parts of the sterols separated from rapeseed oil R by thin-layer chromatography add 1 part of cholesterol R. To the mixture add a freshly prepared mixture of 0.04 mL of chlorotrimethylsilane R, 0.1 mL of hexamethyldisilazane R and 0.5 mL of anhydrous pyridine R. Allow to stand for at least 5 min and use the liquid phase.
Reference solution (b) To the sterols separated from sunflower oil R by thin-layer chromatography add a freshly prepared mixture of 0.04 mL of chlorotrimethylsilane R, 0.1 mL of hexamethyldisilazane R and 0.5 mL of anhydrous pyridine R. Allow to stand for at least 5 min and use the liquid phase.
Carrier gas hydrogen for chromatography R or helium for chromatography R.
Linear velocity 30-50 cm/s (hydrogen) or 20-35 cm/s (helium).
Split ratio 1:50 (hydrogen) or 1:100 (helium).
Detection Flame ionisation.
Injection 1 µL.
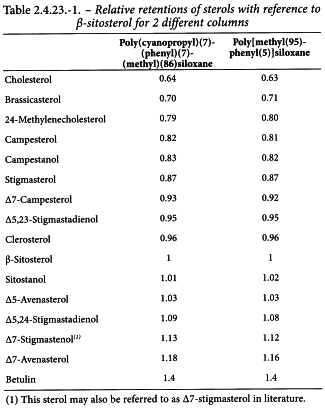
Identification of peaks The chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) shows 4 principal peaks corresponding to cholesterol, brassicasterol, campesterol and β-sitosterol and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) shows 4 principal peaks corresponding to campesterol, stigmasterol, β-sitosterol and Δ7-stigmastenol. The relative retentions of the sterols with reference to β-sitosterol (main peak) are given in Table 2.4.23.-1.
The peak due to the internal standard (betulin) must be clearly separated from the peaks due to the sterols to be determined.
For the chromatogram obtained with the test solution, identify the peaks and calculate the percentage content of each sterol in the sterol fraction of the substance to be examined using the following expression:
| A | = | area of the peak due to the component to be determined; |
| S | = | sum of the areas of the peaks due to the components indicated in Table 2.4.23.-1; disregard the peak due to betulin. |
If required in the monograph, calculate the content of each sterol in milligrams per 100 grams of the substance to be examined using the following expression:
| A | = | area of the peak due to the component to be determined; |
| A′ | = | area of the peak due to betulin; |
| m | = | mass of the sample of the substance to be examined, in grams; |
| m′ | = | mass of betulin R added, in milligrams. |
Method B
Preparation of the unsaponifiable matter
Prepare the unsaponifiable matter according to the method stated in the test for unsaponifiable matter of the monograph on the substance to be examined. Failing this, prepare the unsaponifiable matter according to the method described in chapter 2.5.7. Unsaponifiable matter. After the final neutralisation step, evaporate the ethanol, then add 6 mL of acetone R and evaporate the solvent. Dry the residue at 100-105 °C. It is not necessary to dry to constant mass.
Simultaneously prepare under the same conditions the unsaponifiable matter of sunflower oil R. This will in particular serve to locate the sterol fraction to be collected.
Separation of the sterol fraction (LC)
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution Take up the residue with 3 quantities, each of 4 mL, of the solvent used during the preparation of the unsaponifiable matter (generally ether R or light petroleum R) and transfer to a 15 mL tube. Evaporate to dryness under a current of nitrogen R. Dissolve the residue in a volume of mobile phase sufficient to obtain a solution with an approximate concentration of 40 mg/mL. Add a few drops of 2-propanol R1 to improve the solubility (3 drops are normally sufficient to ensure complete solubilisation). Filter through a membrane filter (nominal pore size 0.45 µm).
Reference solution Proceed as described for the test solution with the unsaponifiable matter obtained with sunflower oil R.
Mobile phase 2-propanol R1, hexane R (1:99 V/V).
Flow rate 1 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 210 nm.
Injection 50 µL.
Identification of the peaks due to sterols The sterol fraction elutes at the end of the chromatogram. Locate the fraction to be collected using the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution, which shows 2 principal peaks eluting approximately between 23 min and 32 min. Collect the fraction at the detector outlet in a 15 mL tube with a screw cap. Evaporate the solvent under a current of nitrogen R.
Determination of the sterols (GC)
Test solution Dissolve the residue of the sterol fraction obtained with the test solution in the previous LC step in 0.2 mL of anhydrous pyridine R and 0.2 mL of a mixture of 1 volume of chlorotrimethylsilane R and 99 volumes of N,O-bis(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide R. Stopper the tube tightly and heat at 80 °C for 20 min. Allow to cool and use the liquid phase.
Reference solution Dissolve the residue of the sterol fraction obtained with the reference solution in the previous LC step in 0.2 mL of anhydrous pyridine R and 0.2 mL of a mixture of 1 volume of chlorotrimethylsilane R and 99 volumes of N,O-bis(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide R. Stopper the tube tightly and heat at 80 °C for 20 min. Allow to cool and use the liquid phase.
A standard of cholesterol (cholesterol R) may also be used, alone or as a mixture with the sterol fraction of sunflower oil. Proceed with derivatisation as described for the test solution.
Carrier gas helium for chromatography R.
Flow rate 2.6 mL/min.
Split ratio 1:25.
Detection Flame ionisation.
Injection 1-3 µL (depending on the expected amount of sterols in the substance to be examined).
Identification of peaks Use the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution to identify the peaks due to campesterol, stigmasterol, β-sitosterol and Δ7-stigmastenol. Identify the peaks due to the sterols in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution using the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution and the relative retentions with reference to β-sitosterol (main peak) given in Table 2.4.23.-1.
Calculate the percentage content of each sterol in the sterol fraction of the substance to be examined using the following expression:
| A | = | area of the peak due to the component to be determined; |
| S | = | sum of the areas of the peaks due to the components indicated in Table 2.4.23.-1, except betulin. |