Turpentine Oil
Preparation
Ph Eur
DEFINITION
Essential oil obtained by steam distillation, followed by rectification at a temperature below 180 °C, from the oleoresin obtained by tapping Pinus pinaster Aiton and/or Pinus massoniana D.Don. A suitable antioxidant may be added.
CHARACTERS
Appearance
Clear, colourless or pale yellow liquid.
Odour reminiscent of α-pinene and β-pinene.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: B
Second identification: A
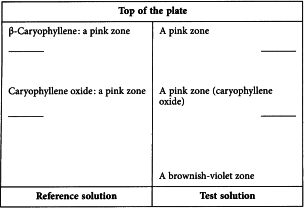
Test solution Dilute 1 mL of the oil to be examined in 10 mL of toluene R.
Reference solution Dissolve 10 µL of β-caryophyllene R and 10 µL of caryophyllene oxide R in 10 mL of toluene R.
PlateTLC silica gel plate R (5-40 µm) [or TLC silica gel plate R (2-10 µm)].
Mobile phaseethyl acetate R, toluene R (5:95 V/V).
Application 10 µL [or 2 µL] as bands of 10 mm [or 8 mm].
Development Over a path of 15 cm [or 6 cm].
Drying In air.
Detection Treat with anisaldehyde solution R and heat at 100-105 °C for 5-10 min; examine in daylight.
Results See below the sequence of zones present in the chromatograms obtained with the reference solution and the test solution. Furthermore, other faint zones may be present below the zone due to caryophyllene oxide in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution.
Results The peaks in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution are similar in retention time to those in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).
TESTS
Relative density (2.2.5)
0.856 to 0.872.
Refractive index (2.2.6)
1.465 to 1.475.
Optical rotation (2.2.7)
-40° to -28°.
Acid value (2.5.1)
Maximum 1.0.
Peroxide value (2.5.5, Method B)
Maximum 20.
Fatty oils and resinified essential oils (2.8.7)
It complies with the test.
Chromatographic profile
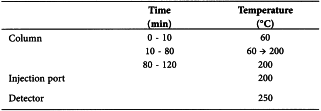
Gas chromatography (2.2.28): use the normalisation procedure.
Test solution Dilute 1.0 mL of the oil to be examined in heptane R and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (a) Dissolve 30 µL of α-pinene R, 10 mg of camphene R, 20 µL of β-pinene R, 10 µL of car-3-ene R, 10 µL of β-myrcene R, 20 µL of limonene R, 10 µL of longifolene R, 10 µL of β-caryophyllene R and 10 mg of caryophyllene oxide R in 1.0 mL of heptane R.
Reference solution (b) Dissolve 5 µL of β-caryophyllene R in heptane R and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 0.1 mL of the solution to 1.0 mL with heptane R.
Carrier gashelium for chromatography R.
Flow rate 1.0 mL/min.
Split ratio 1:200.
Detection Flame ionisation.
Injection 1.0 µL.
Elution order Order indicated in the composition of reference solution (a); record the retention times of these substances.
Using the retention times determined from the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a), locate the components of reference solution (a) in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution.
Determine the percentage content of these components. The limits are within the following ranges:
Residue on evaporation (2.8.9)
Maximum 2.5 per cent, determined after heating on a water-bath for 3 h.
STORAGE
At a temperature not exceeding 25 °C.
Ph Eur