Heparin Injection
Action and use
Anticoagulant.
Definition
Heparin Injection is a sterile solution of Heparin Calcium or Heparin Sodium in Water for Injections. The pH of the solution may be adjusted by the addition of a suitable alkali.
Production
The final product is produced from the drug substance where the methods of manufacturing are designed to ensure freedom from contamination by over-sulfated glycosaminoglycans. The production method is validated to demonstrate that the product if tested, would comply with the test for Related substances given below.
Potency
The estimated potency is not less than 90% and not more than 111% of the stated potency.
Characteristics
A colourless or straw-coloured liquid, free from turbidity and from matter that deposits on standing.
Identification
Tests
Acidity or alkalinity
pH, 5.5 to 8.0, Appendix V L.
Related substances
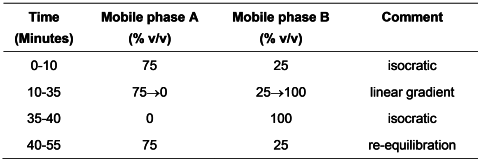
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D using the following solutions. Solutions (3) to (6) are stable at room temperature for 24 hours.
Mobile phase A 0.040% w/v of sodium dihydrogen orthophosphate in water for chromatography adjusted to pH 3.0 with dilute orthophosphoric acid.
Mobile phase B 0.040% w/v of sodium dihydrogen orthophosphateand 14% w/v of sodium perchlorate in water for chromatography, adjusted to pH 3.0 with dilute orthophosphoric acid, filtered and degassed.
Equilibrate the column with the mobile phase in the initial gradient ratio for at least 15 minutes.
When the chromatograms are recorded under the prescribed conditions the retention times relative to heparin (retention time about 26 minutes) are: dermatan sulfate and chondroitin sulfate, about 0.9; over-sulfated chondroitin sulfate, 1.3.
The test is not valid unless:
in the chromatogram obtained with solution (5), no peak is present at the retention time of heparin;
in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (6), the resolution between the peaks due to dermatan sulfate / chondroitin sulfate and over-sulfated chondroitin sulfate is at least 3.0.
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (2):
the area of the peak due to dermatan sulfate and chondroitin sulfate is not greater than the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (6) (2.0%);
no peaks other than the peak due to dermatan sulfate and chondroitin sulfate are detected.
Bacterial endotoxins
Carry out the test for bacterial endotoxins, Appendix XIV C.
For a preparation supplied in a container with a nominal content of less than 100 mL, dilute the injection if necessary with water BET to give a solution containing 1000 IU of heparin activity per mL (solution A). The endotoxin limit concentration of solution A is 10 IU of endotoxin per mL. Carry out the test using a lysate with a declared sensitivity not less sensitive than 0.0625 IU of endotoxin per mL.
For a preparation supplied in a container with a nominal content of 100 mL or more, the endotoxin limit concentration is 0.25 IU of endotoxin per mL.
For Heparin Injection prepared from Heparin Calcium it may be necessary to add divalent cations in order to achieve the validation criteria.
Assay
Carry out the assay of anti-factor IIa activity of heparin, Appendix XIV J B2. The fiducial limits of error are not less than 80% and not more than 125% of the stated potency.
Storage
Heparin Injection should be kept in a container sealed by fusion of the glass.
Labelling
The strength is stated as the number of IU (Units) in a suitable dose-volume except that for multi-dose containers the strength is stated as the number of IU (Units) per mL.
The label states (1) whether the material is the calcium or sodium salt; (2) when no antimicrobial preservative is present that the preparation contains no antimicrobial preservative and that any portion of the contents not used at once should be discarded.